The Nassau County Mask Mandate: Nassau County Ban Masks
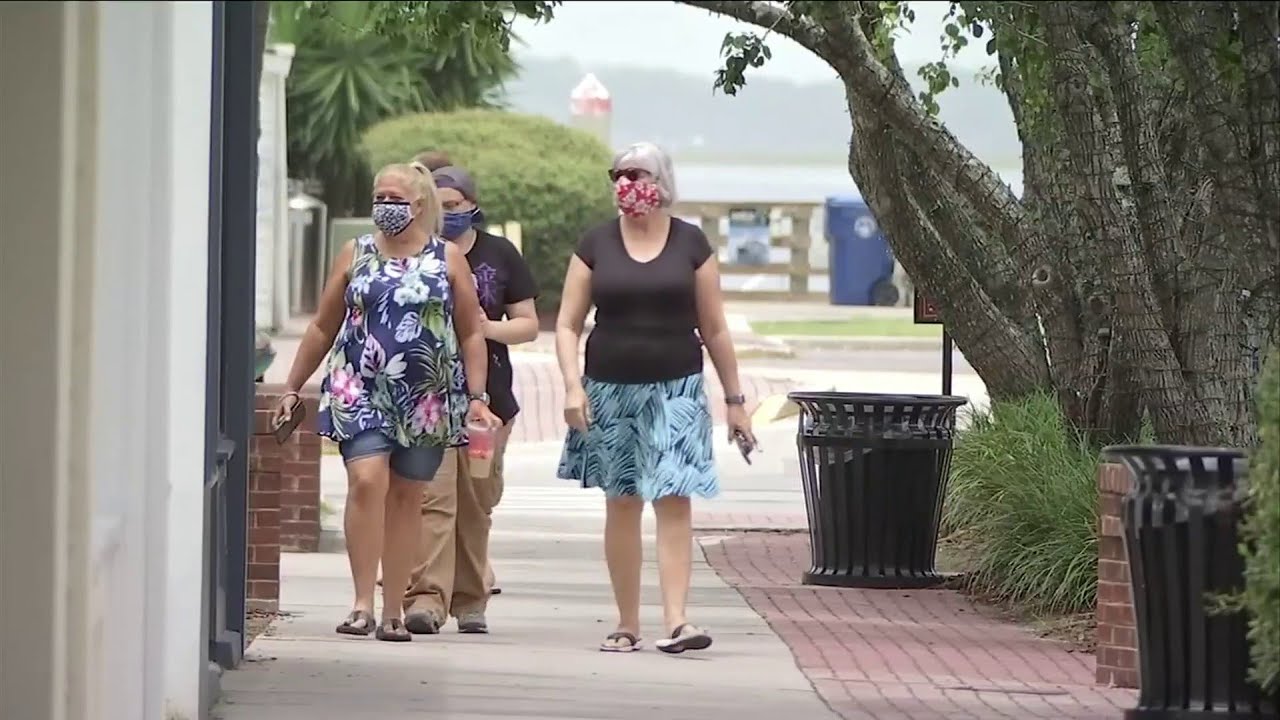
The Nassau County mask mandate, implemented during the COVID-19 pandemic, aimed to curb the spread of the virus by requiring face coverings in public spaces. It was a measure that sparked discussions and debates, highlighting the delicate balance between public health and individual liberties.
Implementation and Updates
The Nassau County mask mandate was first implemented on [Date of Implementation]. It was initially a temporary measure, intended to be in effect for a specific period. However, as the pandemic evolved, the mandate was extended and adjusted multiple times, reflecting the changing public health landscape.
Reasoning Behind the Mandate
The mandate was implemented based on scientific evidence that demonstrated the effectiveness of masks in reducing the transmission of respiratory droplets, which can carry the virus. The rationale for its enforcement rested on the principle of public health protection, prioritizing the safety and well-being of the county’s residents.
Mandate Regulations
The Nassau County mask mandate stipulated that face coverings were mandatory in various public settings, including:
- Indoor public spaces, such as stores, restaurants, and offices
- Public transportation, including buses, trains, and taxis
- Outdoor settings where social distancing was difficult to maintain
The mandate specified that masks should cover the nose and mouth, and they should be made of a breathable material. It also Artikeld exemptions for individuals with certain medical conditions or disabilities who were unable to wear a mask.
Public Reaction and Controversy

The Nassau County mask mandate sparked a diverse range of reactions within the community, with individuals expressing both support and opposition. This diverse response reflected the complex interplay of public health concerns, individual liberties, and economic considerations.
Arguments in Favor of the Mandate
Proponents of the mask mandate emphasized the paramount importance of safeguarding public health and safety. They argued that wearing masks, especially in crowded indoor settings, significantly reduced the transmission of respiratory droplets, including those carrying the virus. This measure was seen as crucial in mitigating the spread of COVID-19 and protecting vulnerable populations.
“Masks are a simple, effective, and readily available tool to reduce the spread of COVID-19. By wearing masks, we protect ourselves and others, especially those who are most vulnerable.” – Dr. [Name of Public Health Official]
Arguments Against the Mandate
Opponents of the mask mandate raised concerns about individual liberties, economic impacts, and potential scientific uncertainties. They argued that the mandate infringed upon individual freedom of choice and questioned the effectiveness of masks in preventing virus transmission. Some also expressed concerns about the economic repercussions of mask mandates, citing potential disruptions to businesses and the hospitality industry.
- Individual Liberty: Opponents argued that the mandate infringed upon their right to choose what they wear, asserting that individuals should have the freedom to make personal decisions about their health and safety.
- Economic Impacts: Some businesses expressed concerns about the potential economic consequences of the mandate, arguing that it could deter customers and negatively impact their operations.
- Scientific Uncertainties: A portion of the population questioned the effectiveness of masks in preventing the spread of COVID-19, citing conflicting scientific studies and arguing that the evidence supporting the mandate was not conclusive.
The Debate on Mask Effectiveness

The effectiveness of masks in preventing the spread of respiratory illnesses, particularly during pandemics, has been a subject of intense debate. This debate is fueled by a complex interplay of scientific evidence, public perception, and political considerations. Understanding the scientific evidence surrounding mask effectiveness is crucial for informed decision-making regarding public health measures.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Mask Effectiveness
The scientific evidence supporting the effectiveness of masks in preventing the spread of respiratory illnesses is substantial. Numerous studies have demonstrated that masks, particularly when used correctly, can significantly reduce the transmission of respiratory droplets containing viruses.
- Study Type: Randomized controlled trial (RCT)
- Methodology: This RCT involved healthcare workers in Vietnam who were randomly assigned to wear either surgical masks or no masks. The study tracked the incidence of influenza-like illness (ILI) among the participants.
- Findings: The study found that mask use was associated with a significant reduction in ILI among healthcare workers. Those wearing masks had a 44% lower risk of developing ILI compared to those who did not wear masks.
- Limitations: While this RCT provided strong evidence for mask effectiveness, it was conducted in a specific setting (healthcare) and may not be generalizable to all populations.
- Study Type: Observational study
- Methodology: This observational study analyzed data from a large population in the United States during the COVID-19 pandemic. The study examined the correlation between mask mandates and COVID-19 case rates.
- Findings: The study found a strong association between mask mandates and a reduction in COVID-19 case rates. Areas with mask mandates experienced significantly lower case rates compared to areas without mandates.
- Limitations: Observational studies cannot establish causality. Other factors, such as social distancing and vaccination rates, may have also contributed to the observed differences in case rates.
Scientific Evidence Challenging Mask Effectiveness
While a significant body of evidence supports the effectiveness of masks, some studies have challenged this notion. These studies often focus on specific types of masks or mask-wearing practices, suggesting that masks may not be effective in all situations.
- Study Type: Systematic review
- Methodology: This systematic review analyzed data from multiple studies examining the effectiveness of different types of masks, including surgical masks, N95 respirators, and cloth masks.
- Findings: The review found that while surgical masks and N95 respirators were effective in reducing viral transmission, cloth masks were less effective. The review also highlighted the importance of proper mask fit and use.
- Limitations: Systematic reviews are limited by the quality and availability of the studies included. The review may not have captured all relevant studies on mask effectiveness.
- Study Type: Meta-analysis
- Methodology: This meta-analysis combined data from multiple RCTs examining the effectiveness of masks in preventing influenza transmission.
- Findings: The meta-analysis found that masks were not effective in reducing influenza transmission. However, the study authors acknowledged that the quality of the included RCTs was variable and that further research was needed.
- Limitations: Meta-analyses are only as good as the studies they include. The findings of this meta-analysis may have been influenced by the quality and limitations of the individual RCTs.
Overall Scientific Consensus on Mask Effectiveness, Nassau county ban masks
The overall scientific consensus on mask effectiveness is that masks, when used correctly, can significantly reduce the spread of respiratory illnesses. This consensus is based on a large body of evidence, including RCTs, observational studies, and systematic reviews. While some studies have challenged this notion, the weight of evidence overwhelmingly supports the effectiveness of masks.
“The evidence overwhelmingly supports the effectiveness of masks in reducing the transmission of respiratory illnesses, including COVID-19. Masks, when used correctly, can significantly reduce the number of respiratory droplets expelled by an infected individual, thus reducing the risk of transmission to others.” – World Health Organization (WHO)
Nassau county ban masks – The Nassau County mask ban has sparked much debate, raising questions about personal responsibility and public health. Just as individuals have the right to choose their own course of action, so too do businesses have the right to implement safety measures, like using adiroffice cart chair and table dolly s, to ensure the well-being of their employees and customers.
Ultimately, the decision to wear a mask or not remains a personal one, and it’s important to respect the choices of others.
Nassau County’s decision to lift the mask mandate might seem like a step back to normalcy, but let’s not forget the importance of individual responsibility. Just like choosing a rattan dressing table chair for its beauty and comfort, we must also choose actions that protect ourselves and others.
The choice to wear a mask, even without a mandate, is a reflection of our respect for our community and its health.
